Manténgase sano!
- Posted August 1, 2025
Coming Soon: An At-Home Patch to Spot Skin Cancers?
Someday, you might apply a small patch onto your skin to find out whether that odd little spot is a cancer or not.
That’s the hope from a new technology being developed by researchers at the University of Michigan.
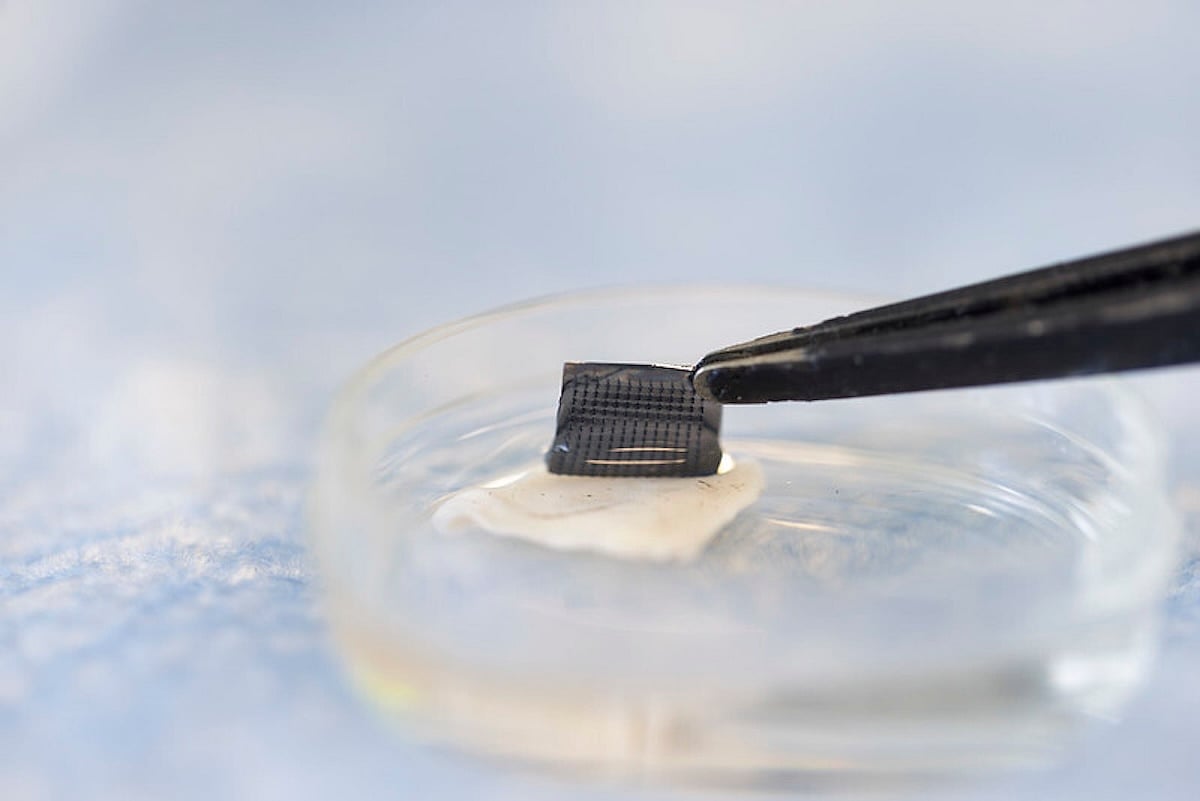
The tiny silicone patch is embedded with micro needles that test the lesion for the presence of biomarker compounds that might signal cancer.
The device, called the ExoPatch, has already proven successful in distinguishing melanomas from healthy tissues in mice.
If successful, it could revolutionize skin cancer detection, said study co-senior author Sunitha Nagrath, professor of chemical engineering at the university.
"A fair-skinned person with moles must [now] go to the doctor about every six months to send off a biopsy to see if they’re malignant or benign,” she explained in a news release. “With this test, they could instead test at home, get the results right away and follow up with a dermatologist for a positive result.”
A study on the new technology is published in the October 2025 issue of the journal Biosensors and Bioelectronics.
The new patch tests what are known as exosomes, microscopic packages released by cells (including skin cells) that contain bits of genetic material that can be related to cancer.
Each ExoPatch contains a gel that attracts skin cell exosomes to microneedles on the patch. After the patch is removed, it’s placed in an acid that allows the exosomes to be released into a solution.
Similar to how at-home COVID tests work, a test strip dipped into the solution will reveal two bars if signs of melanoma are present, or just one bar if they are not.
No blood is needed, the research team stressed.
"The star-shaped needles make puncture easier and less painful, but they are so small that they only go through the top-most layer of the skin, the epidermis, and do not draw blood," Nagrath said.
Studies were conducted in mice — some that were cancer-free and some that had been injected with a fragment of a human melanoma tumor.
The result: Exopatch could effectively tell which mouse skin was cancerous versus noncancerous, with a 3.5-fold darker line forming after contact with melanoma-laden samples.
“This is the first patch designed to capture disease-specific exosomes from fluid under the skin. The potential applications are huge,” Nagrath said.
A pilot study in humans is planned, to be followed by clinical trials. Results of research conducted in animals may differ in humans.
The research is funded by the U.S. National Institutes of Health, and the resesarch team has applied for patent protection.
More information
Find out more about melanoma at the American Cancer Society.
SOURCE: University of Michigan, news release, July 28, 2025





